|
If your email box does not support HTML letter, please visit below URL to access the full version of this letter in browser. www.aimspress.com/Release/collection_math1.html |
 |
|
The collection includes 11 papers with high citations, covering topics such as predator-prey model, Gauss sums, neural networks, Kirchhoff-type problem, mathematical model, nonlinear dynamics, and other mathematical applications. Welcome to the first series of articles suggested. Hope it can be of service of you.
AIMS Mathematics is Open Access and an international monthly publication devoted to publishing peer-reviewed, high quality, research articles, as well as review articles, related to all aspects of the theory and applications of mathematics. To be published in this journal, an original paper must be correct, new, nontrivial and of interest to a substantial number of readers. Every effort is made to ensure a rigorous but quick editorial process and a rapid publication.
|
|
Featured articles
Ruizhi Yang, Dan Jin, Wenlong Wang*
Time delay in the resource limitation of the prey is incorporated into a diffusive predator-prey model with generalist predator. By analyzing the eigenvalue spectrum, time delay inducing instability and Hopf bifurcation are investigated. Some conditions for determining the bifurcation direction and the stability of the bifurcating periodic solution are obtained by utilizing the normal form method and center manifold reduction for partial functional differential equation. The results suggest that time delay can destabilize the stability of coexisting equilibrium and induce bifurcating periodic solution when it increases through a certain threshold.
|
|
Kaihong Zhao*
In this paper, we build a novel nonlinear diffusion online game addiction model with unsustainable control. The existence and boundedness of a solution are investigated by a C0-semigroup and differential inclusion. Simultaneously, we study the global asymptotic stability of steady states of the model. Finally, a concrete example is theoretically analyzed and numerically simulated.
|
|
Wenpeng Zhang, Xiaodan Yuan*
In this paper, we use the analytic methods and the properties of the classical Gauss sums to study the calculating problems of some Gauss sums involving the character of order 12 modulo an odd prime p, and obtain several new and interesting identities for them.
|
|
Chao Wang, Fajie Wang*, Yanpeng Gong*
This paper proposes a local semi-analytical meshless method for simulating heat conduction in nonlinear functionally graded materials. The governing equation of heat conduction problem in nonlinear functionally graded material is first transformed to an anisotropic modified Helmholtz equation by using the Kirchhoff transformation. Then, the local knot method (LKM) is employed to approximate the solution of the transformed equation. After that, the solution of the original nonlinear equation can be obtained by the inverse Kirchhoff transformation. The LKM is a recently proposed meshless approach. As a local semi-analytical meshless approach, it uses the non-singular general solution as the basis function and has the merits of simplicity, high accuracy, and easy-to-program. Compared with the traditional boundary knot method, the present scheme avoids an ill-conditioned system of equations, and is more suitable for large-scale simulations associated with complicated structures. Three benchmark numerical examples are provided to confirm the accuracy and validity of the proposed approach.
|
|
Justin Eilertsen, Marc R. Roussel, Santiago Schnell, Sebastian Walcher*
The conditions for the validity of the standard quasi-steady-state approximation in the Michaelis–Menten mechanism in a closed reaction vessel have been well studied, but much less so the conditions for the validity of this approximation for the system with substrate inflow. We analyze quasi-steady-state scenarios for the open system attributable to singular perturbations, as well as less restrictive conditions. For both settings we obtain distinguished invariant manifolds and time scale estimates, and we highlight the special role of singular perturbation parameters in higher order approximations of slow manifolds. We close the paper with a discussion of distinguished invariant manifolds in the global phase portrait.
|
|
Anti-periodic dynamics on high-order inertial Hopfield neural networks involving time-varying delays
Qian Cao, Xiaojin Guo*
Taking into accounting time-varying delays and anti-periodic environments, this paper deals with the global convergence dynamics on a class of anti-periodic high-order inertial Hopfield neural networks. First of all, with the help of Lyapunov function method, we prove that the global solutions are exponentially attractive to each other. Secondly, by using analytical techniques in uniform convergence functions sequence, the existence of the anti-periodic solution and its global exponential stability are established. Finally, two examples are arranged to illustrate the effectiveness and feasibility of the obtained results.
|
|
Ya-Lei Li, Da-Bin Wang*, Jin-Long Zhang
In this paper, we study the existence of ground state sign-changing solutions for following p-Laplacian Kirchhoff-type problem with logarithmic nonlinearity
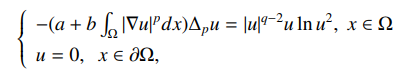 where Ω ⊂ RN is a smooth bounded domain, a,b > 0 are constant, 4 ≤ 2p < q < p∗ and N > p. By using constraint variational method, topological degree theory and the quantitative deformation lemma, we prove the existence of ground state sign-changing solutions with precisely two nodal domains. |
|
Xavier Bardina, Marco Ferrante, Carles Rovira*
To model the evolution of diseases with extended latency periods and the presence of asymptomatic patients like COVID-19, we define a simple discrete time stochastic SIR-type epidemic model. We include both latent periods as well as the presence of quarantine areas, to capture the evolutionary dynamics of such diseases.
|
|
Zachary Abernathy*, Kristen Abernathy, Jessica Stevens
We present a system of four nonlinear differential equations to model the use of virotherapy as a treatment for cancer. This model describes interactions among infected tumor cells, uninfected tumor cells, effector T-cells, and virions. We establish a necessary and sufficient treatment condition to ensure a globally stable cure state, and we additionally show the existence of a cancer persistence state when this condition is violated. We provide numerical evidence of a Hopf bifurcation under estimated parameter values from the literature, and we conclude with a discussion on the biological implications of our results.
|
|
Zihan Li, Xiao-Bao Shu*, Fei Xu
In this article, we consider the existence of upper and lower solutions to a second-order random impulsive differential equation. We first study the solution form of the corresponding linear impulsive system of the second-order random impulsive differential equation. Based on the form of the solution, we define the resolvent operator. Then, we prove that the fixed point of this operator is the solution to the equation. Finally, we construct the sum of two monotonic iterative sequences and prove that they are convergent. Thus, we conclude that the system has upper and lower solutions.
|
|
Thomas P. Witelski*
Fluid films spreading on hydrophobic solid surfaces exhibit complicated dynamics that describe transitions leading the films to break up into droplets. For viscous fluids coating hydrophobic solids this process is called "dewetting". These dynamics can be represented by a lubrication model consisting of a fourth-order nonlinear degenerate parabolic partial differential equation (PDE) for the evolution of the film height. Analysis of the PDE model and its regimes of dynamics have yielded rich and interesting research bringing together a wide array of different mathematical approaches. The early stages of dewetting involve stability analysis and pattern formation from small perturbations and self-similar dynamics for finite-time rupture from larger amplitude perturbations. The intermediate dynamics describes further instabilities yielding topological transitions in the solutions producing sets of slowly-evolving near-equilibrium droplets. The long-time behavior can be reduced to a finite-dimensional dynamical system for the evolution of the droplets as interacting quasi-steady localized structures. This system yields coarsening, the successive re-arrangement and merging of smaller drops into fewer larger drops. To describe macro-scale applications, mean-field models can be constructed for the evolution of the number of droplets and the distribution of droplet sizes. We present an overview of the mathematical challenges and open questions that arise from the stages of dewetting and how they relate to issues in multi-scale modeling and singularity formation that could be applied to other problems in PDEs and materials science.
|
| If you have a WeChat, please pay close attention to AIMS Press, and you can visit https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bCWnTOr4vEvnK60QSRenpg | |
| Journal Home https://www.aimspress.com/journal/Math Email: mathematics@aimspress.org |
|
| 2022 Impact Factor | 2.2 |
| 2022 CiteScore | 3 |
 |